State the Two Laws of Thermal Radiation.
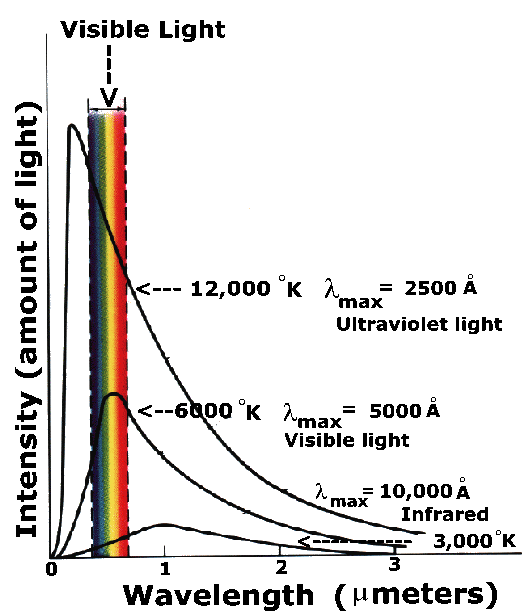
As the source temperature gets higher the wavelength of peak exitance moves towards shorter wavelengths. For an arbitrary body emitting and absorbing thermal radiation in thermodynamic equilibrium the emissivity is equal to the absorptivity.
A black body to its surroundings is proportional to the fourth power of the absolute temperature and can be expressed by the following equation.

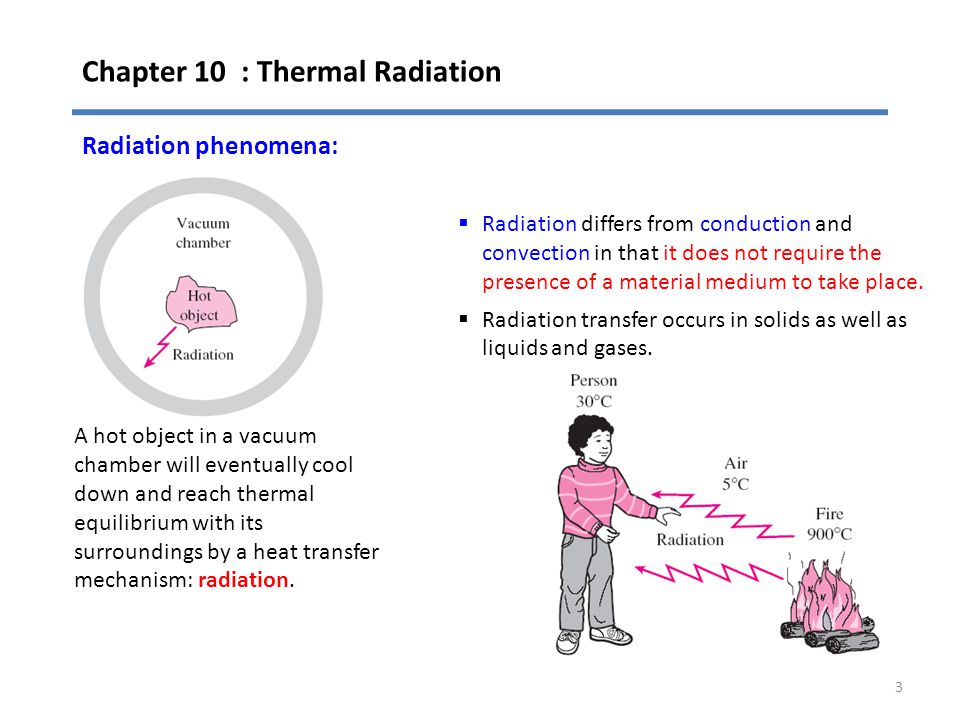
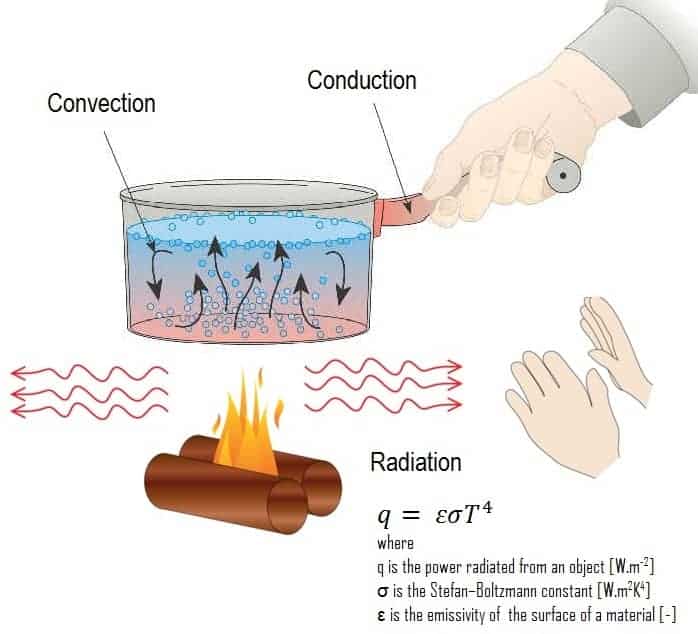
. This is because radiation occurs through electromagnetic waves and they do not need a medium for transmission. Thermal radiation reflects the conversion of thermal energy into electromagnetic energyThermal energy is the kinetic energy of random movements of atoms and molecules in matter. Q εσT 4.
Law for Thermal Conduction in Steadt State. Kirchhoffs Law of thermal radiation. As was written all bodies above absolute zero temperature radiate some heat.
As a result of this law heat cannot spontaneously flow from cold system to hot system and the second law of thermodynamics is still satisfied. So rate of flow of heat will be Δ Q Δ t T 1 T 2 L K A. State and prove Kirchhoffs law.
Plancks law describes the electromagnetic radiation emitted by a black body in thermal. Emissivity ε absorptivity α. Law 1 Stefan-Boltzmann law.
Concept of gray body has been presented. 4 Main Laws of Radiation 1. A perfect black body in thermodynamic equilibrium absorbs all light that strikes it and radiates energy.
Consider the following thought experiment. Where σ is a fundamental physical constant called the StefanBoltzmann constant which is equal to 5669710-8 Wm 2 K 4. We derive four laws relating the absorptivity and emissivity of thermal emitters.
Any grey object other than a perfect black body which receives radiation disposes off a part of it. Theoretical proof of Kirchhoffs law of thermal radiation. Hotter objects emit brighter light.
The proofs exploit two recent approaches. How the Laws of Thermal Radiation Work 1. Equality of emissivity and absorptivity has been established.
Complete step by step answerThe properties of thermal radiation are. In heat transfer Kirchhoffs law of thermal radiation refers to wavelength-specific radiative emission and absorption by a material body in thermodynamic equilibrium including radiative exchange equilibrium. In summary thermal radiation is governed by the following two laws.
In steady state ΔQ amount of heat passing through a bar of length L and cross-section A in Δt time when its ends are at temperatures T 1 and T 2 is given by. Δ Q Δ t T 1 T 2 R T h. The temperature of the suns surface is around 5800K.
Kirchhoffs Law of thermal radiation. The Stefan Boltzmann law describes the power radiated R from a black body in terms of its temperature T. Unlike Conduction and Convection Thermal Radiation requires no medium to transfer heat.
The wavelength of the spectral peak is proportional to T-1 Thermal Radiation Rayleigh-Jeans approximation. Law 2 Wiens law. Emissivity ε absorptivity α.
Radiation heat transfer rate q Wm 2 from a body eg. Weins displacement law is given in the next section. Intensity vs wavelength follows the idealized black-body radiation curve Stefan-Boltzmann law.
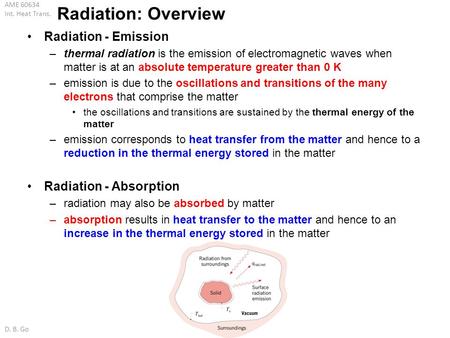
Thermal radiation is the emission of electromagnetic waves from all matter that has a temperature greater than absolute zero. Each square meter of a hotter objects surface emits more light at all wavelengths. All matter with a nonzero temperature is composed of.
An ordinary body A and a perfectly black body B are enclosed in an athermanous enclosure as shown in figure. This law must be also valid in order to satisfy the Second Law of Thermodynamics. Kirchoffs law states that the ratio of the emissive power to absorptive power for the radiation of a given wavelength is constant for all substances at the same temperature.
This constant is equal to the emissive power of a perfectly black body at the same temperature and corresponding to the same wavelength. Hotter objects emit photons with a higher average energy which means a shorter average wavelength-which is why the peaks of the spectra are at shorter wavelengths for hotter objects. Kirchhoffs law of heat radiation.
Hotter objects emanate light with a more limited wavelength and a higher frequency. At a given temperature the ratio of the emissive power to the coefficient of absorption of a body is equal to the emissive power of a perfect blackbody at the same temperature for all wavelengths. Total energy emitted over time by a black body is proportional to T4 Wiens displacement law.
4 basic laws about radiation 1Planck Radiation Law. Thermal radiation transmitted by a body at any temperature comprises a wide scope of frequencies. Hotter things produce light having more brightness.
Thermal radiation is administered by the two laws. The StefanBoltzmann law states that the total energy radiated per unit surface area of a. Kirchhoffs law of radiation.
Hotter objects emit light with a shorter wavelength and a higher frequency. The Two Laws of Thermal Radiation. Δ Q Δ t K A T 1 T 2 L.
After some interval of time both A and B will attain the same temperature as that of the enclosure. We will consider two bodies A and B being suspended in a constant temperature enclosure. Lamberts cosine law has been presented and utilized to determine intensity of radiation in terms of total emissive power of a blackbody.
At a given temperature the coefficient of absorption of a body is equal to its coefficient of emission. Prevost heat exchange theory states that every body will emit and absorb. The heat that the Earth receives from the sun is through Radiation.
λ m T 2898 where T is in kelvins and λ m is in micrometers. Kirchhoffs Law has been stated and proved. Unlike the original Kirchhoff radiation law derivations these derivations include diffraction and so are valid also for small objects and can also cover nonreciprocal objects.
The Stefan-Boltzmann Law The first law of thermal radiation states that each square meter of a hotter objects. Wiens Law The second law of thermal radiation says that a hotter object will emit photons that have a higher. Thermal Radiation has another interesting property.
According to the Stefan Boltzmann law The rate of emission of radiant energy per unit area or the power radiated per unit area of a perfect blackbody is directly proportional to the fourth power of its absolute temperature. For a body emitting and absorbing thermal radiation in thermal equilibrium the emissivity is equal to its absorptivity. A body at temperature T radiates electromagnetic energy.
For an arbitrary body emitting and absorbing thermal radiation in thermodynamic equilibrium the emissivity is equal to the absorptivity. The peak of the spectral distribution curve is at 98 µm for a blackbody at room temperature. This law states that the intensity of radiation emitted by a radiating body is proportional to.
A is a normal material body and B is a perfectly black body.

How To How The Laws Of Thermal Radiation Work Space Com Forums
Chapter 12 Thermal Radiation Ppt Video Online Download

Introduction To Thermal Radiation And Radiation Heat Transfer Ppt Download

Introduction To Thermal Radiation And Radiation Heat Transfer Ppt Download
What Is Radiation Heat Transfer Definition

What Are The 3 Ways Heat Can Be Transferred Radiation Transfer By Electromagnetic Waves Conduction Transfer By Molecular Collisions Convection Transfer Ppt Download

Chapter 12 Fundamentals Of Thermal Radiation Ppt Download
Fundamentals Of Thermal Radiations
Introduction To Thermal Radiation And Radiation Heat Transfer Ppt Download
No comments for "State the Two Laws of Thermal Radiation."
Post a Comment